Previously …
Recap
At this point, we have written a smart contract, and have also written some tests using mocha, that are unrelated to the smart contract. We've done that intentionally, so as to learn the fundamentals of each technology separately.
Now, we are about to combine the two - truffle comes with a test runner that is a wrapper around Mocha. Truffle's edition of Mocha comes with some conveniences that make it possible to test smart contracts easily.
Project environment
Truffle Project
If you still have the dadc-cars project set up from the previous session,
you may re-use it.
Otherwise, follow the instructions in the introduction to truffle hands-on.
Before proceeding with the next steps of this hands-on, we strongly suggest that you commit your repository at in its current state, that is after writing the smart contract, but before writing any tests, before proceeding.
This will be very similar to the Version control with git section of the introduction to mocha hands-on.
Environment
NodeJs
Ensure that you have NodeJs installed, and is either version eight or ten. You can check the version using:
$ node -v
v8.12.0$ node -v
v10.15.0If you have a UNIX-based operating system, you can install and switch between different versions of NodeJS using nvm.
Python
In addition to this, make sure that you do not have python 3 on your PATH
while doing anything that requires node-gyp
(for example, while installing truffle),
as node-gyp assumes python 2 only.
Ganache
In a previous session, we used ganache to run
a simulated Ethereum network on localhost, and we made the distinction
between truffle console --network development and truffle develop -
as we wished to connect to ganache, we used the former.
Truffle has the ability to run its own simulated Ethereum network on
localhost as well, and if we wanted to make use of that,
we would use the latter.
When we run tests via truffle, it expects to connect to an existing Ethereum network, and not need to spin up its own one, thus we must start ganache and ensure that it is running before proceeding.
Test structure
Create a new file which we will use to write our specification for
the Cars smart contract:
touch test/Cars.spec.jsOpen this file, and enter the structure of a truffle test.
const Cars = artifacts.require('Cars');
const BN = web3.utils.BN;
contract('Cars - data storage', (accounts) => {
// tests go here
});Comparing mocha to truffle
We notice that there are a lot of similarities between a standard mocha test, and also the fact that there are some differences.
-
Referencing the implementation
- In both, the specification needs to reference the implementation.
- In mocha, we use a standard
require(CommonJS standard), or animport(ES Modules). - In truffle, we use
artifacts.require, which returns a wrapped-by-truffle copy of the Solidity smart contract that is a Javascript object.
-
Grouping of tests
- In both, we can group similar or related tests together using function blocks.
- In mocha, this is a
describeblock. - In truffle, this is a
contractblock.
-
Group function parameters
- In both, the first parameter is a string that describes the group
- Mocha
describeblock's second parameter is a function that has zero parameters. - Truffle's
contractblock's second parameter is a function that has one parameter - a list of available accounts on the Ethereum network
-
Group function body
- In mocha's
describeblock, you can put tests or otherdescribeblocks inside its function body. - In truffle's
contractblock, you can put tests inside its body.
- In mocha's
Running the tests
Right now, we have zero tests, but let's just run them anyway, to make sure that we have done our set up correctly:
truffle testIf the output looks like this, you either do not have ganache running, or your truffle configuration does not work:
Could not connect to your Ethereum client with the following parameters:
- host > 127.0.0.1 - port > 8545 - network_id > 5777Please check that your Ethereum client:
- is running
- is accepting RPC connections (i.e., "--rpc" option is used in geth)
- is accessible over the network
- is properly configured in your Truffle configuration file (truffle-config.js)If your output looks like this, it means all good!
Using network 'development'.
Compiling your contracts...
===========================
> Compiling ./contracts/Cars.sol
> Compiling ./contracts/Migrations.sol
> Artifacts written to /var/folders/_9/ywg4bs883rd1zfh0n5544rr40000gn/T/test-119322-6582-10yrtmy.w73y
> Compiled successfully using:
- solc: 0.5.0+commit.1d4f565a.Emscripten.clang
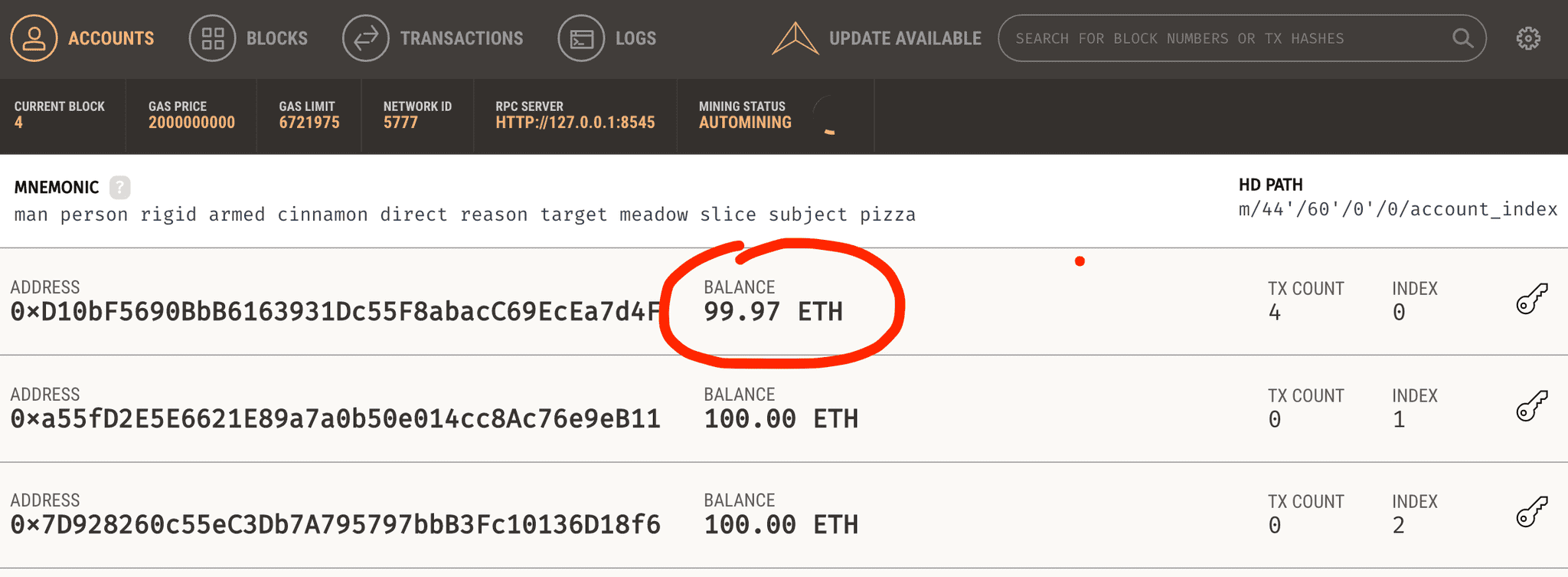
0 passing (0ms)Also, be sure to check ganache to ensure that the balance has decreased:
This happened because the first account, being the default one that truffle makes use of for its operations, had to pay gas costs related to the deployment of the smart contract - this is really just a sanity check, to make sure that we are indeed connecting to the Ethereum network (ganache on localhost) which we think we are.
Congratulations
🎉🎉🎉 You have got truffle test runner to work.
Next, we will write out first tests.